AVISO LEGAL Y FINALIDAD DE LA PÁGINA WEB
En cumplimiento del artículo 10 de la Ley 34/2002, de 11 de julio, de Servicios de la Sociedad de la Información y Comercio Electrónico (LSSICE) se detallan los datos identificativos de la entidad
ELESAPIENS LEARNING & FUN, S.L., con C.I.F. B-86432101 y domicilio social en c/ c/ Orense 20, 2-10, 28020, Madrid. España, inscrita en el Registro Mercantil de Madrid el 24 de abril de 2.012, en el Tomo 29.859, folio 143, hoja número M-537264, inscripción 1ª, es una empresa dedicada a producir y comercializar productos educativos y de entretenimiento digitales. A través de este aviso legal se pretende regular el acceso y uso, y en general, la relación entre este sitio web, accesible en la dirección de Internet http://www.elesapiens.com, y los usuarios del sitio web.
CONDICIONES GENERALES DE USO DEL SITIO WEB
Las Condiciones Generales regulan el uso del sitio web de ELESAPIENS LEARNING & FUN, S.L., con C.I.F. B-86432101 y domicilio social en c/ Orense 20, 2-10, 28020, Madrid, España, inscrita en el Registro Mercantil de Madrid el 24 de abril de 2.012, en el Tomo 29.859, folio 143, hoja número M-537264, inscripción 1ª, al que se accede mediante la dirección http://www.elesapiens.com.
La existencia de las presentes Condiciones Generales de Uso no excluye la presencia de otras disposiciones o condiciones de acceso a las diversas secciones que componen el sitio de ELESAPIENS LEARNING & FUN, S.L.
Dentro de la expresión “sitio o sitio web” se comprenden -con carácter delimitativo, pero no limitativo- los datos, textos, gráficos, imágenes, animaciones, creaciones musicales, vídeos, sonidos, dibujos, fotografías y otros incluidos en el mismo, y, en general, todas las creaciones expresadas por cualquier medio o soporte, tangible o intangible con independencia de que sean susceptibles o no de propiedad intelectual de acuerdo al Texto Refundido de la Ley de Propiedad Intelectual. Asimismo, también se entenderán incluidos en este sitio web todos los microsites a los que se pueda acceder desde el presente sitio web, excepto que dicho microsite, expresamente recoja unas condiciones de uso propias, en cuyo caso se le aplicarán éstas.
El uso del sitio web de ELESAPIENS LEARNING & FUN, S.L, implica el conocimiento y plena aceptación de las advertencias legales y condiciones vigentes en cada momento en que el usuario acceda al mismo y que a continuación se especifican.
Asimismo, la utilización de determinados servicios a disposición de los usuarios de este sitio oficial puede estar sometida a condiciones especiales, advertencias o instrucciones que también deberán ser consultadas y aceptadas sin reservas por aquellos.
El usuario visitante es consciente de que el acceso y utilización de los servicios y contenidos del sitio se realiza bajo su única y exclusiva responsabilidad.
El usuario utilizará los servicios y contenidos exclusivamente para fines particulares con exclusión de cualquier modalidad de utilización posterior de los mismos con ánimo de lucro o reporte de algún beneficio, directo o indirecto.
En caso de que el usuario no acepte estas condiciones generales o, las condiciones particulares que regulen el uso de un determinado servicio y/o contenido destinado a los usuarios del sitio web y que dicha entidad determine, el usuario deberá abstenerse de acceder al sitio web o en su caso abandonarlo.
Con carácter general los servicios y contenidos ofrecidos a través del sitio web estarán disponibles en español e inglés, sin perjuicio de la posibilidad que se reserva ELESAPIENS de ofrecer los mismos en otros idiomas oficiales.
ELESAPIENS podrá modificar de forma unilateral y sin aviso previo, la prestación, configuración, contenido y servicios del sitio, así como sus condiciones de uso y el acceso a los contenidos ofrecidos y servicios prestados.
Derechos y obligaciones del usuario
El usuario podrá:
- Acceder de forma gratuita y sin necesidad de autorización previa a los contenidos y servicios del sitio disponibles como tales, sin perjuicio de las condiciones técnicas, particulares o la necesidad del previo registro respecto de servicios y contenidos específicos según se determine en estas condiciones generales o en las condiciones particulares de dichos servicios.
- Utilizar los servicios y contenidos disponibles para su uso exclusivamente particular.
- Hacer un uso correcto y lícito del sitio, de conformidad con la legislación vigente, la moral, las buenas costumbres y el orden público.
Si solicitamos información de registro al usuario, este deberá ofrecernos una información verdadera, precisa, actual y completa. Deberá actualizar a tiempo su información de registro para mantenerla exacta, actual y completa. Si se le envía una contraseña, no debe revelarla a nadie más. El usuario no usará contraseñas de otras personas, siendo responsable de mantener la confidencialidad de sus cuentas y contraseñas. El usuario acepta notificarnos inmediatamente sobre cualquier uso no autorizado de sus contraseñas, cuentas o cualquier otra infracción de seguridad. También acepta cerrar la sesión de sus cuentas a final de cada sesión. No seremos responsables de cualquier pérdida o daño originado por su incumplimiento de estos requisitos.
El usuario no podrá realizar cualquier acción que suponga la reproducción, distribución, copia, alquiler, comunicación pública, transformación o cualquier otra acción similar que suponga la modificación o alteración, de todo o parte de los contenidos y servicios del sitio o la explotación económica de los mismos, sin la autorización previa y por escrito de ELESAPIENS o de terceros propietarios de los derechos de propiedad intelectual e industrial que recaigan sobre los servicios o contenidos del sitio web y a salvo de lo dispuesto en estas condiciones generales o, en su caso, condiciones particulares que regulen el uso de un servicio y/o contenido existente en el sitio web.
Sin limitar lo dicho anteriormente, el usuario se compromete a no usar nuestra página para hacer lo siguiente:
- Utilizar la marca, nombres comerciales, así como cualquier otro signo identificativo que se encuentre sujeto a derechos de propiedad intelectual o industrial, sin la previa autorización expresa y por escrito de su propietario.
- Utilizar los servicios y contenidos ofrecidos a través del sitio de forma contraria a las condiciones generales de uso y/o las condiciones particulares que regulen el uso de un determinado servicio y/o contenido, y en perjuicio o con menoscabo de los derechos del resto de usuarios.
- Difamar, insultar, acosar, perseguir, amenazar o de otra manera violar los derechos legales de otras personas;
- Publicar, exponer, subir, enviar por correo electrónico, distribuir o divulgar (colectivamente, “Transmitir”) cualquier contenido no apropiado, profano, difamatorio, obsceno, indecente o ilegal;
- Enviar archivos que contienen virus, archivos dañados o cualquier otro software similar, o programas que pueden dañar o afectar de una manera negativa el funcionamiento del ordenador de otra persona, página web, cualquier software o hardware, u otro equipo.
- Enviar encuestas, concursos, sistemas piramidales, correo no deseado, anuncios no solicitados, materiales de promoción o cadenas de mensajes;
- Descargar cualquier archivo que el usuario sabe o razonablemente debe saber que no se puede obtener legalmente de tal manera;
- Falsificar o eliminar cualquier atributo de autor, avisos legales o designaciones propietarias, etiquetas de origen, código fuente de software u otro material;
- Restringir o prohibir a cualquier usuario usar y disfrutar de cualquier área pública dentro de nuestra página web;
- Entrometerse en nuestra página web o trastornarla;
- Falsificar encabezados o manipular identificadores u otros datos para ocultar el origen de cualquier contenido transmitido a través de nuestra página web o manipular su presencia en nuestra página web.
- Realizar cualquier acción que resulta ser causa de una carga excesiva o desproporcionadamente larga de nuestro servidor o equipos;
- Eliminar o modificar de cualquier modo los dispositivos de protección o identificación de ELESAPIENS o sus legítimos titulares que puedan contener los contenidos alojados en el sitio web, o los símbolos que ELESAPIENS o los terceros legítimos titulares de los derechos incorporen a sus creaciones objeto de propiedad intelectual o industrial existentes en este sitio web.
- Reproducir total o parcialmente el presente sitio web en otro sitio web distinto; no podrá realizar enmarcados al presente sitio o los sitios web accesibles a través del mismo que oculten o modifiquen con carácter delimitativo, pero no limitativo- contenidos, espacios publicitarios y marcas de ELESAPIENS o de terceros, con independencia o no de que supongan actos de competencia desleal o de confusió
- Estar involucrado en actividades ilegales.
Usted acepta la condición de usar nuestros foros, comunidad y/o servicios de comunicación o mensajería (conjuntamente, los “Foros) sólo para enviar y recibir mensajes e información adecuada y relacionada con un Foro particular.
Si selecciona un nombre de usuario que, según nuestra opinión, es obsceno, indecente, insultante o que puede ser la causa de descrédito o desdén público, reservamos el derecho de cambiar automáticamente su nombre de usuario sin notificación previa, eliminar sus publicaciones en nuestras páginas web, prohibirle el acceso a la página web o cualquier combinación de estas opciones.
La utilización del sitio oficial deberá obedecer al contenido de estas Condiciones Generales, y a cualesquiera disposiciones legales aplicables.
ELESAPIENS se reserva el derecho unilateral de denegar el acceso a este sitio web a aquellos usuarios que incumplan las presentes Condiciones Generales de Uso.
Derechos y obligaciones de ELESAPIENS
ELESAPIENS se reserva los siguientes derechos:
- Modificar las condiciones de acceso al sitio, técnicas o no, de forma unilateral y sin preaviso a los usuarios, sin perjuicio de lo dispuesto en las condiciones particulares que regulen el uso de un determinado servicio y/o contenido destinado a los usuarios del sitio web.
- Establecer condiciones particulares y, en su caso, la exigencia de un precio u otros requisitos para el acceso a determinados servicios y/o contenidos.
- Limitar, excluir o condicionar el acceso de los usuarios cuando no se den todas las garantías de utilización correcta del sitio por los mismos conforme a las obligaciones y prohibiciones asumidas por los mismos.
- Finalizar la prestación de un servicio o suministro de un contenido, sin derecho a indemnización, cuando su utilización por los usuarios devenga ilícito o contrario a lo establecido en las condiciones que lo regulan, sin perjuicio de lo dispuesto en las condiciones particulares que regulen el uso de un determinado servicio y/o contenido destinado a los usuarios del sitio web.
- Modificar, suprimir o actualizar todo o parte de los contenidos o servicios ofrecidos a través del sitio, sin necesidad de preaviso, sin perjuicio de lo dispuesto en las condiciones particulares que regulen el uso de un determinado servicio y/o contenido destinado a los usuarios del sitio web.
- Emprender cualquier acción legal o judicial que resulte conveniente para la protección de los derechos de ELESAPIENS como de terceros que presten sus servicios o contenidos a través del sitio, siempre que resulte procedente.
- Exigir la indemnización que pudiera derivar por el uso indebido o ilícito de todo o parte de los servicios y contenidos prestados a través del sitio.
Exención y limitación de responsabilidad de ELESAPIENS
ELESAPIENS S.L queda exenta de cualquier tipo de responsabilidad por daños y perjuicios de toda naturaleza en los siguientes casos:
- Por la imposibilidad o dificultades de conexión a la red de comunicaciones a través de la que resulta accesible este sitio web, independientemente de la clase de conexión utilizada por el usuario.
- Por la interrupción, suspensión o cancelación del acceso al sitio web, así como por disponibilidad y continuidad del funcionamiento del sitio o de los servicios y/o contenidos en el mismo, cuando ello se deba (i) bien a interrupción del servicio por mantenimiento técnico de la web, (ii) bien a una causa ajena al ámbito de control de ELESAPIENS ya provenga directa o indirectamente de ésta.
- ELESAPIENS no asume ninguna responsabilidad respecto de los servicios y contenidos, ni por la disponibilidad y condiciones, técnicas o no, de acceso a los mismos, que sean ofrecidos por terceros prestadores de servicios, en especial respecto de los prestadores de servicios de la sociedad de la información. Por prestadores de servicios de la sociedad de la información se entenderán aquellas personas físicas o jurídicas que presten los siguientes servicios al público: (i) transmisión por una red de comunicación de datos facilitados por el destinatario del servicio (ii) servicios de acceso a la citada red (iii) Servicios de almacenamiento o alojamiento de datos (iv) suministro de contenidos o información (v) servicio de copia temporal de los datos solicitados por los usuarios (vi) facilitación de enlaces a contenidos o instrumentos de búsqueda.
- Del tratamiento y utilización posterior de datos personales realizados por terceros ajenos a ELESAPIENS, así como la pertinencia de la información solicitada por éstos.
- De la calidad y velocidad de acceso al sitio y de las condiciones técnicas que debe reunir el usuario con el fin de poder acceder al sitio y a sus servicios y/o contenidos.
- ELESAPIENS, no será responsable de los retrasos o fallos que se produjeran en el acceso y/o funcionamiento de los servicios y/o contenidos del sitio web, debido a un caso de Fuerza Mayor. “Caso de fuerza mayor” significará todas aquellas causas que no hayan podido preverse, o que aún previstas fueran inevitables, y que dan como resultado el incumplimiento de cualesquiera de sus obligaciones. Entre ellas, pero no de forma limitativa, las huelgas, tanto de sus propios trabajadores como de trabajadores ajenos, insurrecciones o revueltas, así como normas dictadas por cualquier autoridad civil o militar, catástrofes naturales como terremotos, inundaciones, rayos o incendios, guerras, cierres patronales o cualquier otra situación de fuerza mayor.
- El usuario del sitio responderá personalmente de los daños y perjuicios de cualquier naturaleza causados a ELESAPIENS directa o indirectamente, por el incumplimiento de cualquiera de las obligaciones derivadas de estas condiciones generales u otras normas por las que se rija la utilización del sitio.
Propiedad intelectual e industrial
El usuario conoce que los contenidos y servicios ofrecidos a través del sitio -incluyendo textos, gráficos, imágenes, animaciones, creaciones musicales, vídeos, sonidos, dibujos, fotografías, todos los comentarios, exposiciones y código informático de la misma, sin que esta enumeración tenga carácter limitativo- se encuentran protegidos por las leyes de propiedad intelectual e industrial. El derecho de autor y de explotación económica de este sitio corresponde a ELESAPIENS y/o terceras entidades.
Las marcas, nombres comerciales o signos distintivos que aparecen en el sitio web son propiedad de ELESAPIENS y/o en su caso, de terceras entidades, y se encuentran protegidos por las leyes vigentes de propiedad industrial.
La prestación de los servicios y publicación de los contenidos a través del sitio no implicará en ningún caso la cesión, renuncia o transmisión, total o parcial, de la titularidad de los correspondientes derechos de propiedad intelectual e industrial por ELESAPIENS y/o sus terceros legítimos titulares.
Ningún apartado de este sitio web puede ser reproducido, distribuido, transmitido, copiado, comunicado públicamente, transformado, en todo o en parte mediante ningún sistema o método manual, electrónico o mecánico (incluyendo el fotocopiado, grabación o cualquier sistema de recuperación y almacenamiento de información) a través de cualquier soporte actualmente conocido o que se invente en el futuro, sin consentimiento de ELESAPIENS. La utilización, bajo cualquier modalidad, de todo o parte del contenido del sitio queda sujeta a la necesidad de solicitar autorización previa de ELESAPIENS y/o terceros titulares legítimos y la aceptación de la correspondiente licencia, en su caso, excepto para lo dispuesto respecto de los derechos reconocidos y concedidos al usuario en estas condiciones generales o lo que así se determine en las condiciones particulares que ELESAPIENS tenga a bien establecer para regular el uso de un determinado servicio y/o contenido ofrecido a través del sitio web.
Contenidos y materiales publicados por el usuario
El usuario se compromete a no introducir, almacenar o difundir mediante este sitio web, cualquier contenido que infrinja derechos de propiedad intelectual o industrial, ni en general ningún contenido respecto del cual no ostenten, de conformidad con la ley, el derecho a ponerlo a disposición de terceros.
No obstante, ELESAPIENS podrá modificar los contenidos, a fin de adaptarlos a las necesidades de formato editorial del sitio web.
ELESAPIENS no se hará responsable de las opciones de disposición que elija el usuario respecto de los contenidos que aloje, poniendo a disposición de los mismos un espacio para que éstos incorporen sus contenidos y los compartan con otros usuarios, no controlando tampoco si los contenidos infringen o no los derechos mencionados en los párrafos anteriores.
Hiperenlaces
El uso de hiperenlaces al presente sitio web únicamente será autorizado por ELESAPIENS mediante autorización escrita y siempre que el hiperenlace se realice en los siguientes términos previstos en las presentes condiciones:
Protección de datos personales
ELESAPIENS garantiza la confidencialidad de los datos de carácter personal facilitados por los usuarios y su tratamiento de acuerdo a la legislación vigente sobre protección de datos de carácter personal: Reglamento (UE) 2016/679, de 27 de abril, General de Protección de Datos. Los datos personales recogidos a través del sitio web serán incorporados a uno o varios tratamientos responsabilidad de ELESAPIENS. A tales efectos, se proporcionará a los usuarios, con carácter previo a la entrega de los datos personales a través de este sitio web, información sobre el tratamiento sin perjuicio de la posibilidad del usuario de acceder a la Política de Privacidad y Protección de Datos de Carácter Personal. La información antedicha permitirá al usuario otorgar su consentimiento informado, específico e inequívoco a fin de que ELESAPIENS proceda al tratamiento de sus datos personales.
TERMINACIÓN
Si bien, en principio, la duración de este sitio es indeterminada, ELESAPIENS se reserva el derecho a suspender o dar por terminada la prestación de algunos o todos sus servicios, sin que esta decisión deba ser comunicada con antelación a los usuarios del mismo.
LEY Y JURISDICCIÓN APLICABLE
Estas condiciones generales se rigen por la legislación española.
Las partes, con expresa renuncia a su propio fuero, se someten para la resolución de cuantos litigios pudieran derivarse a los Juzgados y Tribunales de Madrid (España).
CONTRATACIÓN DE UN PLAN DE SUSCRIPCIÓN PREMIUM
Para contratar un Plan de Suscripción Premium de ELESAPIENS LEARNING & FUN, S.L., es necesario conectarse a http://www.elesapiens.com, y registrarse como usuario, cumplimentando el formulario electrónico que en cada momento aparezca en la página web de la tienda y siguiendo las instrucciones indicadas en el mismo. ELESAPIENS pone a disposición del usuario todos los medios técnicos necesarios para identificar y corregir errores en la introducción de sus datos en los diferentes formularios que aparecerán en la pantalla durante el proceso de contratación.
Tras el registro, deberá seleccionar el plan y el periodo de suscripción que deseé contratar haciendo clic en botón “Suscribir” correspondiente, según las indicaciones recogidas en pantalla, cumplimentando a estos efectos el formulario de suscripción suministrado, incluida la forma de pago, y validando el mismo. Una vez validada la suscripción no podrán modificarse los datos facilitados para la contratación del plan y periodo seleccionados por el cliente.
Los precios y ofertas presentados en el website son válidos única y exclusivamente para suscripciones online realizadas en http://www.elesapiens.com y pueden no coincidir con los precios y ofertas vigentes en otras tiendas. Todos los precios publicados en nuestra página web son con impuestos indirectos incluidos.
La validación de la suscripción por parte del cliente supone expresamente el conocimiento y aceptación de estas condiciones generales de contratación como parte de la celebración del contrato. Salvo prueba en contrario, los datos registrados por ELESAPIENS constituyen la prueba del conjunto de transacciones realizadas entre ELESAPIENS y sus clientes. ELESAPIENS archivará el documento electrónico en que se formalice el contrato y éste será accesible.
Una vez efectuado por el cliente el pago de la suscripción al plan que haya elegido recibirá, en la dirección de correo electrónico que nos haya facilitado, un email de confirmación de la suscripción. En su cuenta online podrá comprobar toda la información y el estado de su suscripción.
El cliente podrá solicitar a ELESAPIENS la factura o el comprobante de la suscripción contratada.
ELESAPIENS advierte que no se podrán modificar las facturas de suscripción una vez emitidas, sin perjuicio del derecho a obtener factura rectificativa en los supuestos previstos en la normativa vigente (Real Decreto 1619/2012, de 30 de noviembre que aprueba el Reglamento por el que se regulan las obligaciones de facturación). La factura se emite a nombre de la persona física o empresa que aparece en la dirección de facturación cuando se realiza la suscripción, por lo que debe asegurarse de realizar el pedido con la dirección de facturación correcta.
El cliente una vez valide la suscripción, no podrá cancelarla.
Durante el periodo que dure la suscripción contratada, el cliente tiene a su disposición contratar la suscripción de un plan superior.
El cliente tendrá acceso a los contenidos del plan de suscripción contratado durante el periodo contratado. Ninguna suscripción se renueva automáticamente, por lo que el cliente después de la expiración de la suscripción deberá volver a suscribirse a dicho plan mediante el proceso de contratación establecido.
Medios de pago
ELESAPIENS. le propone diversos medios de pago para que pueda elegir aquel que más le convenga o se adapte mejor a sus necesidades:
Pago por Tarjeta de Crédito: Puede utilizar Visa y Mastercard.
Pago por Transferencia: Esta modalidad de pago está limitada a suscriptores del plan School.
Pago con PayPal: Este método de pago, le permite pagar con su cuenta de PayPal de forma rápida y segura, sin compartir información financiera con ELESAPIENS. Será redirigido a la web segura de PayPal, donde introducirá las credenciales de tu cuenta PayPal, aceptando el pago y después a www.elesapiens.com, donde le confirmaremos su suscripción.
SUSCRIPCIÓN DE UN PLAN GRATUITO
Para suscribirse a un Plan de Suscripción Gratuito de ELESAPIENS LEARNING & FUN, S.L., como el plan Basic, en las condiciones establecidas por ELESAPIENS, es necesario conectarse a http://www.elesapiens.com, y registrarse como usuario, cumplimentando el formulario electrónico que en cada momento aparezca en la página web de la tienda y siguiendo las instrucciones indicadas en el mismo. ELESAPIENS pone a disposición del usuario todos los medios técnicos necesarios para identificar y corregir errores en la introducción de sus datos en los diferentes formularios que aparecerán en la pantalla durante el proceso de suscripción.
La suscripción a un Plan de Suscripción Gratuito, supone expresamente el conocimiento y aceptación de las condiciones de acceso a los contenidos de dicho Plan por el usuario.
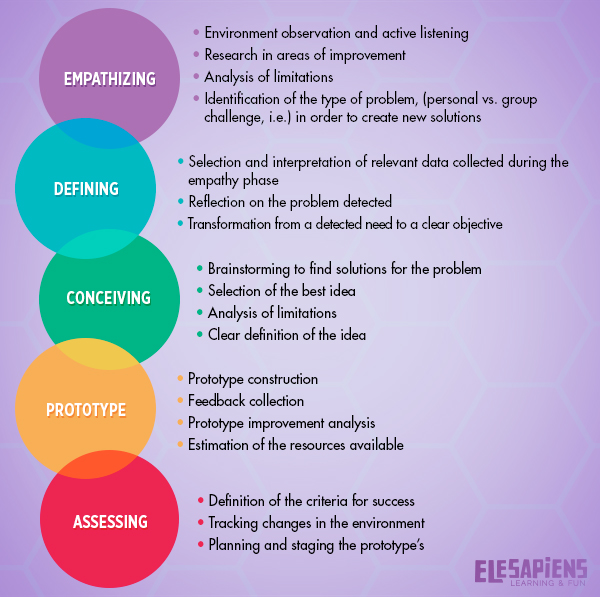

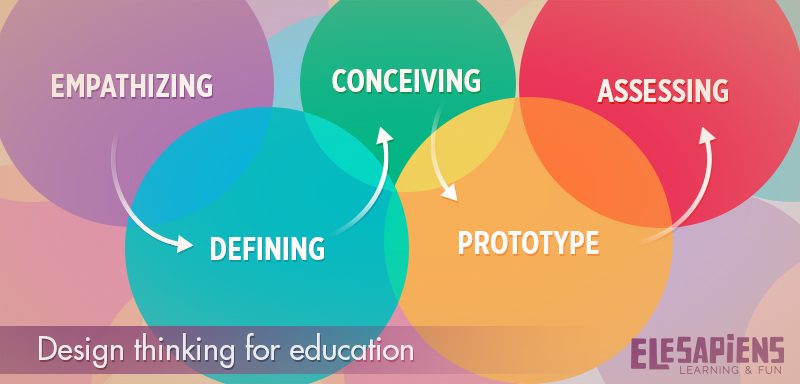





Pingback: Design thinking ili 'dizajnersko promišljanje' u edukaciji - Školski portal - Centar školskog svijeta
Pingback: Design thinking ili 'dizajnersko promišljanje' u edukaciji - Školski portal - Centar školskog svijeta
Pingback: Design thinking ili 'dizajnersko promišljanje' u edukaciji - Školski portal - Centar školskog svijeta